Would you like to replace your missing teeth with implants?
Dental implants are the best method for tooth replacement, but they are not suitable for everyone. Tooth loss can significantly impact a person’s quality of life, affecting functional aspects such as chewing and speaking, as well as causing aesthetic discomfort.
Dental implants are a popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth and are now offered in many dental clinics. However, this method is not suitable for everyone. Certain physical and medical conditions may prevent a person from undergoing this surgery.
So, who is not a good candidate for dental implants? In this article, we will examine which individuals are not suitable for dental implants. If you are also looking for a suitable method to replace missing teeth, don’t miss this article. Stay with us.
Who is not a suitable candidate for dental implants?
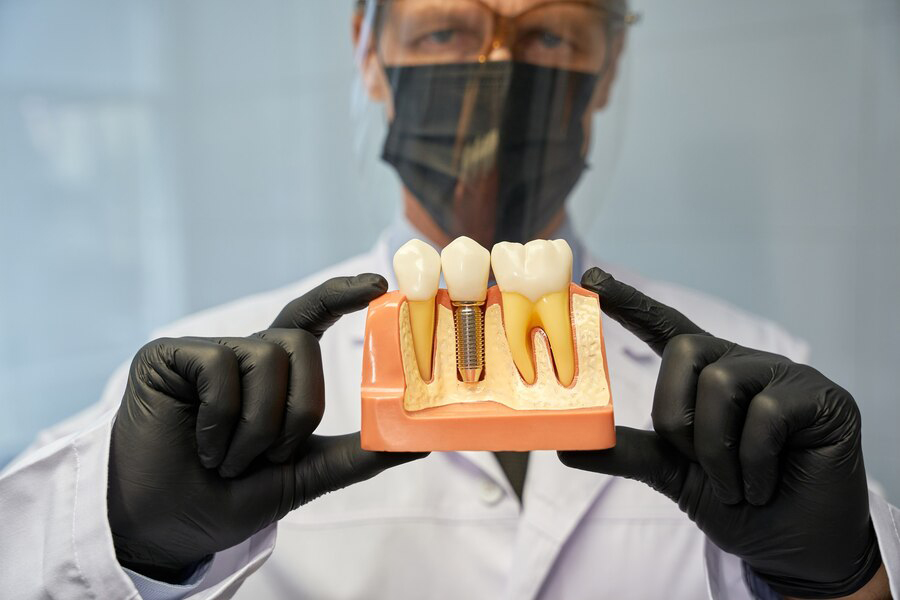
Dental implants are an advanced dental procedure that restores both facial aesthetics and tooth functionality. However, not everyone can use this method to replace missing teeth. Below, we will discuss conditions that may disqualify someone from being a good candidate for dental implants. Keep in mind that the final decision rests with the dentist.
1. People with uncontrolled diabetes
One of the key factors in determining a suitable candidate for dental implants is blood sugar control in diabetic patients. Uncontrolled diabetes can severely affect wound healing. In such patients, wound recovery often takes much longer, increasing the risk of serious infections, bleeding, and other complications.
Since dental implants require quick and proper gum healing, any disruption in this process can lead to unfavorable outcomes. If a person can manage their diabetes through medication and dietary changes, they may still qualify for implants, but any treatment should be performed under medical supervision.
2. People with cardiovascular diseases
Patients with heart and vascular diseases should also be cautious when choosing a method for tooth replacement. These patients may face an increased risk of post-surgical complications, especially if they are taking blood thinners or other specific medications.
Surgery in these patients may lead to problems such as heart failure or stroke. Therefore, the treating physician must evaluate all aspects to ensure the patient’s safety before proceeding with implants.
3. People with gum disease
Gum health plays a crucial role in the success of dental implants. Patients with active gum disease, infections, or inflammation in the surrounding tissues face a higher risk of implant failure. Gum disease can lead to serious issues, such as implant loosening or movement, and negatively affect post-surgical healing.
If any infection or gum disease is detected, it must be treated first. Only after ensuring gum health can dental implants be considered.
4. People with weakened immune systems
A compromised immune system can significantly impact the success of dental implants. Individuals with conditions such as HIV/AIDS, autoimmune diseases, leukemia, or multiple sclerosis may face numerous challenges during the implant process.
When an implant is placed in the jawbone, the body must naturally respond to the healing process. In patients with weakened immune systems, this response is disrupted, leading to poor gum tissue recovery. Improper healing can result in severe infections, which are difficult to control in such patients.
Therefore, these individuals should consult their doctors before considering tooth replacement options.
5. Smokers
Smoking is a major risk factor for dental health and negatively impacts dental treatments, especially implants. Tobacco use reduces blood circulation and impairs oral tissue healing, prolonging recovery time and increasing the risk of post-surgical infections.
Since proper oral hygiene is essential for successful implants, constant exposure to harmful substances in tobacco can lead to periodontal disease, increasing the likelihood of implant failure. Research also shows that smokers are at higher risk of jawbone deterioration due to gum and bone tissue damage, leading to irreversible consequences.
6. Pregnant women
Pregnant women should avoid dental implants. Pregnancy is a sensitive period with significant hormonal and physical changes that can affect overall and dental health. Most dentists recommend avoiding non-emergency surgeries, including dental implants, during pregnancy.
Anesthesia and pain medications used during implant procedures may adversely affect the fetus. Additionally, the stress of surgery can negatively impact pregnancy.
Moreover, X-rays required during implant procedures can be harmful to the fetus. Exposure to radiation poses serious risks, so non-essential dental treatments should be postponed until after pregnancy.
7. People with osteoporosis
Individuals with osteoporosis are also not ideal candidates for dental implants. This disease, which causes bone density loss, can negatively affect implant success. In such patients, the jawbone may be too weak to properly fuse with the implant.
Certain medications, such as bisphosphonates (used to strengthen bones), can further delay bone healing, increasing the risk of implant failure. Therefore, people with osteoporosis may face significant challenges in achieving stable and durable implants.
8. Cancer patients
Cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy or radiation therapy often have weakened immune systems, increasing the risk of severe oral infections. These infections can interfere with the implant process and lead to serious complications.
Generally, cancer patients should not undergo implant procedures immediately after treatment. Studies recommend waiting at least three months after chemotherapy and six months after radiation therapy before considering implants. This waiting period allows the immune system to recover, improving the chances of successful implantation.
Individual factors, such as the type and severity of cancer and treatment, should also be considered. Consulting with both the oncologist and dentist is essential before proceeding.
9. Individuals under 18 years old
Dental implants are not recommended for individuals under 18 because their jawbones are still developing. The jawbone must have sufficient density and strength to properly support an implant.
Placing implants before bone growth is complete increases the risk of implant failure, movement, and the need for additional surgeries. Dentists recommend waiting until at least 18 years of age, when jawbone development is more stable, before considering implants.
Final Thoughts
Dental implants are an effective and often permanent solution for restoring the function and appearance of missing teeth. However, they may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with certain medical conditions.
A thorough evaluation by a dentist before any surgical procedure is essential to minimize risks and ensure successful outcomes. Being aware of these factors can help patients make informed decisions about their dental health.





Leave A Comment